To begin with, let’s clear an oft quoted doubt: “Are workflow management and workflow automation one and the same?”
The answer is no. Workflow management and workflow automation are closely related, but there are a few fundamental differences in their scope and function within business processes. While workflow automation refers specifically to the use of technology to automate repetitive tasks within business processes, thereby reducing or eliminating human intervention, workflow management is the broader function related to designing, organizing, tracking, and optimizing processes, which involves both automated and manual steps.
According to Grand View Research: “The global workflow management system market size was estimated at USD 9,540.0 million in 2022 and is projected to register a CAGR of 33.3% from 2023 to 2030,” to reach almost USD 86.63 billion.
With the rapid developments in technology, AI in workflow management now ensures that tasks are completed in time and in the correct order, also involving the appropriate personnel, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and reducing errors.
Traditional Workflow Management and Its Limitations
While workflow management systems have been crucial in providing a structured approach to managing tasks, traditional systems typically use a rule-based approach and often require manual configurations to establish workflows that align with business processes. Though this approach has enabled businesses to standardize their operations, it often lacks the flexibility and scalability needed to adapt to rapidly changing business environments.
Since traditional systems are based on predefined rules and manual inputs, they face significant challenges, particularly in handling high-volume repetitive tasks that require minimal human intervention. The inflexibility of these systems sometimes lead to tailbacks, and delays, which result in increased operational costs. This also affects the overall customer experience. Furthermore, businesses may struggle to identify and address inefficiencies in their workflows because of its inability to leverage data-driven insights.
Why Use AI in Workflow Management
All the challenges faced by traditional workflow management methods can be addressed to a great extent with the incorporation of AI. By integrating AI to their legacy workflow management systems, enterprises can automate routine tasks, streamline processes, reduce errors, and enhance decision-making by gaining valuable insights.
In addition, companies can employ workflow management software that incorporates AI and machine learning capabilities to adapt workflows in real time and optimize processes for enhanced performance. Also, they help businesses improve their overall efficiency to improve customer experience and retention.
As businesses continue to navigate the complexities of modern markets, embracing innovative workflow management solutions will be key to maintaining a competitive edge.
How AI, Predictive Analytics and Decision Engines Are Transforming Workflow Management?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is redefining how business workflows are managed by enhancing decision-making processes and automating routine tasks. The machine learning algorithms of AI enable systems to learn from data patterns and make informed decisions without human intervention. This also allows seamless integration of AI with existing workflow systems that enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of business operations.
Predictive analytics and decision engines can be generally classified as subsets of the broader AI that further enhances the capabilities of AI, but not always so. While predictive analytics is a technique within the broader AI and data science ecosystem, a decision engine software is a system that automatically makes decisions or recommendations based on data, rules, or predictive models.
One thing to note here is that while predictive analytics and decision engines can be classified as AI, not all predictive analytics and decision engines are purely AI. When predictive analytics uses machine learning or deep learning models, it can be classified as AI. Likewise, only when a decision engine software uses machine learning, predictive analytics, or optimization algorithms, it can be called an AI tool.
Hence, when data analytics depend on only simpler statistical models, or when decision engines are just programmed rules without self-learning, they cannot be classified as AI. However, AI, in general can be called the umbrella technology that manages the others.
How AI Improves Workflow Management
AI-powered workflows have the capability to adapt to changing business environments, allowing for real-time decision-making and adjustments to workflows. By leveraging the power of machine learning algorithms, predictive analytics and decision engines, AI can identify trends, predict outcomes, and recommend actions, thereby enabling businesses to stay ahead of the competition.
The Following are the benefits of AI in workflow management:
- Automating Repetitive Tasks: One of the most significant contributions of AI in workflow management is the automation of repetitive and time-consuming routine tasks, thereby reducing to almost eliminating human intervention. AI ensures seamless response to customer enquiries with the help of automated data collection and analysis. It can process multiple customer requests simultaneously, while also offering personalized responses, enhancing customer experience. This automation process ensures faster response time, minimal errors, and improved efficiency in workflow management.
- Improved Decision-making: AI can seamlessly integrate predictive analytics and decision engine into workflow management systems and help businesses with better and smarter decision-making processes. For example, AI with the help of machine learning, predictive analytics and decision engines can not only study customer behavior but also suggest improvements to the onboarding process to boost productivity and help businesses implement proactive strategies for risk management.
- Workflow Enhancement: AI can enhance the entire workflow by optimizing task assignment, tracking, and completion. It can also put a filter on who can have access to the task thereby ensuring that only authorized people handle the tasks. This helps businesses maintain a steady workflow and reduce their turnaround time.
- Real-time Monitoring and Performance Tracking: AI enables tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) in real time to gain valuable insights into business workflows. For example, it can track customer productivity by analyzing their behavior. It can also detect inefficient workflows that hinder overall productivity and flag potential issues, bottlenecks or other discrepancies so that timely intervention can be made to correct them, thereby optimizing performance through continuous improvements.
- Enhance Team Collaboration: AI can evaluate the progression of an ongoing project and automatically share updates with concerned individuals and also keep everyone in the loop by streamlining communication and sharing.
- Improve Communication: AI-powered virtual assistants, chatbots, and email automation tools help in instant conversational response, reducing manual input and improving communication speed. This in turn improves efficiency and productivity across business workflows.
- Better Customer Experience: AI-enabled CRMs can analyze customer preferences by examining past interactions and customer data to offer personalized recommendations. This works like a personal assistant trying to resolve your issues. This level of personalization enhances the customer experience, leading to higher satisfaction, loyalty, and retention rates.
All these and more by AI goes towards identifying various cost-saving opportunities across the entire workflow. Other than cost savings, the improved efficiency, productivity and personalization that AI brings into business workflows result in a more competent workplace as well as happier customers.
Using Predictive Analytics and AI for Business Process Improvement
Predictive analytics uses historical data combined with statistical modelling, data mining techniques and machine learning to predict future outcomes. Often associated with big data and data science, predictive analytics is employed by companies to detect patterns in data to identify risks and opportunities. It is to be noted that predictive analytics falls under the gamut of AI only when it employs machine learning algorithms to predict future outcomes based on historical records.
There are three types of predictive modelling — Classification, Clustering and Time Series models.
- Classification Models: These come under supervised machine learning models, and they categorize data based on historical data, describing relationships within a given dataset. A practical example is of it being used to classify customers or prospects into groups for segmentation purposes. It can also be used to answer questions with binary outputs like ‘yes’ or ‘no’, or ‘true’ or ‘false’. This model is best used for tasks like credit risk analysis or fraud detection. Logistic regression, random forest, decision tree, Naïve Bayes and neural networks are the types of classification models currently in use.
- Clustering Models: Clustering comes under unsupervised learning and they group data based on similar attributes. For example, the CRM site of a beauty salon can use this model to separate customers into similar groups based on common parameters and develop marketing strategies for each group. Common clustering algorithms include Mean-shift Clustering, K-Means Clustering, density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN), expectation-maximization (EM) clustering using Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM), and hierarchical clustering.
- Time Series Models: This is a supervised mathematical model used to analyze and forecast data points that are collected sequentially over a specific period of time (daily, weekly, monthly, etc.), with the key idea being that past values in the sequence can help predict future values. It is used to examine data for trends, seasonality, and cyclic behavior. For example, an e-commerce site can use this method to forecast how many visitors it will get particularly over weekends and on other specific days. Frequently used time series models are Autoregressive (AR), moving average (MA), ARMA and ARIMA models.
- Neural Networks Models: These are advanced predictive models capable of analyzing complex data patterns and relationships. Examples include Feed Forward Neural Networks, Recurrent Neural Networks, and Convolutional Neural Networks.
An organization that can forecast future outcomes based on past patterns has a business advantage in managing inventories, workforce, marketing campaigns and most other facets of operation.
The following are some of the benefits of predictive analytics:
- Risk Reduction: With its ability to forecast possible future outcomes, predictive analytics can be used by insurance companies to underwrite policies, and to determine the risk factors in approving policies. Similarly, financial services companies that offer credit facilities can use predictive analysis to understand if a customer poses a higher-than-average risk of defaulting.
- Operational Efficiency: More efficient workflow is akin to improved operational efficiency and hence better profit margins. For instance, being able to forecast when a delivery vehicle in a fleet is going to need maintenance before it breaks down on the side of the road means deliveries are made on time, without the additional costs of having the vehicle towed, and bringing in another employee to complete the delivery.
- Security: Data security is a major concern in every modern organization, and predictive analytics with a combination of automation can give peace of mind to business managers. Predictive analytics enables businesses to detect specific patterns associated with suspicious and unusual end user activities and this can trigger specific security procedures.
- Improved Decision-making: Predictive analytics models can provide businesses with insights to help them make learned decisions.
With the help of predictive analytics, businesses can stay ahead of their competition and cash in on new opportunities by forecasting adversities in advance and taking the necessary steps to mitigate them in a dynamically changing business environment.
How Decision Engines Enhance Business Decision-making
In simple words, a decision engine, sometimes referred to as decision tree, is essentially a system or a software that enables automating, streamlining and enhancing decision-making. Decision engines are employed across different industries and use cases, from finance and healthcare to e-commerce and logistics.
An AI-based decision engine can play an important role in enhancing business decisions by automating the decision-making process. It ingresses data, predefined rules, and machine learning algorithms to evaluate complex information and deliver decisions in real time. This tool primarily helps businesses increase efficiency and improve decision quality.
The quality of decisions is improved by decision engines by consistently applying rules and leveraging advanced analytics, which includes predictive models and machine learning algorithms. This consistency also helps in eliminating the variability and bias that often accompany human judgment. Additionally, these engines incorporate real-time data, thereby ensuring that decisions are based on the most current information, enhancing their relevance and accuracy.
Yet another possibility that decision engines (cloud-based) present us with is the scope for scalability and adaptability. As a business grows, the volume of decisions and the complexity of the data involved typically increase. A cloud-based decision engine scales to handle this growth efficiently, adapting its processes to new data sources, business rules, and decision criteria without compromising performance.
The typical data flow in a decision engine can be visualized as follows:
- Data Gathering: Data is collected from various sources and input into the engine.
- Data Pre-processing: Raw data is cleaned, transformed, and validated to prepare it for analysis.
- Rule Evaluation: The engine evaluates predefined rules based on incoming data.
- Decision Analysis: The results of rule evaluation are analyzed to determine the optimal decision.
- Decision Output: The final decision or recommendation is generated.
- Integration: The decision output is integrated into the relevant application or process.
- Feedback Loop: Data on decision outcomes is collected for continuous improvement.
The following are the benefits of decision engines:
- Improved Efficiency: By automating the decision-making process, businesses can reduce to almost eliminate the need for human intervention, which makes the entire process much faster.
- Enhance Performance: The increased speed and accuracy in decision-making helps to free up time and resources for more business-critical functions, thereby optimizing business performance.
- Flexibility: Enables changing decision criteria without having to re-do your entire workflow.
- Scalability: With automation, businesses can handle large volumes of data efficiently and make real-time decisions at scale.
- Reduced Bias: Minimizing human intervention translates to minimizing human biases through algorithmic decision-making based on predefined criteria.
- Improves Agility: Enabling quick responses to changing conditions or new data inputs, helps to improve agility and competitiveness.
Also, there are different types of decision engines tailored to specific business needs and use cases. These types offer flexibility in how decisions are made and can be integrated into different applications. Below are some of the types:
| Decision Engine Type | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Business Rules Engines | Designed to manage and execute business rules efficiently. | Ideal for automating decision-making processes in industries like finance, insurance, and healthcare. |
| Machine Learning Decision Engines | Leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to make decisions based on patterns in data. | Ideal for applications like recommendation systems, fraud detection, and predictive analytics |
| Expert Systems | Mimic human expertise in a specific domain. | Commonly used in healthcare for diagnosing diseases and in customer support for issue resolution. |
| Optimization Decision Engines | Focus on finding the best possible solution from a set of alternatives. | Used in supply chain management, resource scheduling, and financial portfolio optimization. |
| Event-driven Decision Engines | Respond to real-time events and trigger actions or decisions. | Commonly used in IoT (Internet of Things) applications, cybersecurity, and event processing. |
| Policy-based Decision Engines | Enforce predefined policies to guide decision-making. | Commonly found in government, finance, and healthcare sectors to ensure regulatory compliance. |
| Hybrid Decision Engines | Combine multiple decision-making approaches to optimize outcomes. | Ideal for complex decision scenarios where a single approach may be insufficient. |
Businesses can decide which types of decision engine to use depending on the specific requirements of the application, the nature of decision-making processes, and the available data and resources. There are many examples of organizations leveraging multiple types of decision engines to address various aspects of their decision automation needs.
Conclusion
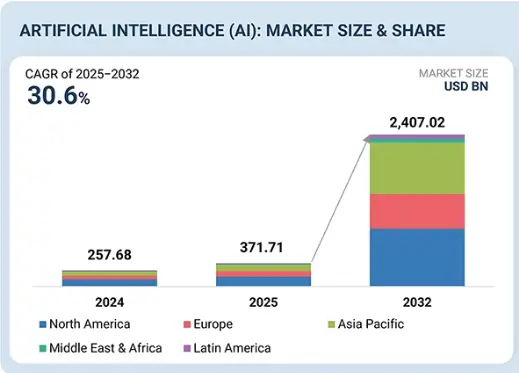
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets: “The global artificial intelligence market size was estimated at USD 371.71 billion in 2025, and is projected to reach USD 2407.02 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 30.6% from 2025 to 2032.”
This shows the scope of applications of AI, and when it comes to workflow management, a judicious use of AI coupled with the right mix of predictive analytics tools and decision engines can give you optimum results.
As mentioned earlier in this post, there is a range of automation and AI tools in the market and if your business needs to manage workflow with intelligent tools, partnering with the right implementation expert can save you a lot of hassles instead of you doing it the trial and miss way. This is where an experienced service provider like DeepKnit AI can help you. With extensive knowledge in AI applications and their implementation, DeepKnit AI can help you achieve your desired goals.
Make Workflow Management Smarter with AI, Predictive Analytics and Decision Engines.
Connect with a DeepKnit AI expert to find out more.
Click here for a consultation