According to Medscape’s “Physician Compensation Report,” overall, physicians spend 15.5 hours per week on paperwork and administration, of which nine hours are on EHR documentation. That’s essentially the same time they are spending away from their core-function, which is patient care.
Besides, this paperwork comes in vast volumes of unstructured and semi-structured data like scanned referrals, patient intake forms, lab reports, handwritten clinical notes, billing documentation, and more. These fragmented data from different systems and formats make sharing and analyzing medical records difficult, challenging collaboration and continuity of care.
Automating medical records with AI has proven to be a solution preferred by an increasing number of healthcare professionals, as it can reduce their burnout, and give them more time to spend on what they are best at doing – patient care.
AI-driven automation tools, especially when combined with Optical Character Recognition (OCR), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) are assisting in clinical safety checks, advising doctors, and managing case notes, thereby increasing efficiency.
The Unintended Burden: EHRs and Clinician Burnout
Digital health systems are mainstream in many markets but challenges remain. For example, in the U.S., 88.2 % of office-based physicians use Electronic Medical Record/Electronic Health Record (EMR/EHR) systems, and 77.8 % use a certified system.
Though EHRs were introduced to digitalize medical records and make life easier for healthcare professionals, it had an unintended downside because usage of an EHR does not mean all documents are fully digital or structured for automation, with many still relying on scanned PDFs, faxed documents, handwritten notes, and ancillary systems.
According to a study conducted by JMIR Medical Informatics, “Within the realm of EHR use, healthcare professional burnout, characterized by emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and a diminished sense of personal accomplishment, has emerged as a critical concern. Some studies have reported an average burnout prevalence of 44%, with rates exceeding 80% in some specific settings and departments such as primary care and emergency departments.”
Specific Pain Points
- Manual effort and human error: To manually classify, transcribe, and enter data is time-consuming and error-prone. For example, one source estimates that there is up to 50% reduction in productivity in manual record-keeping compared to digital workflows.
- Data silos and fragmentation: Patient records are usually spread across multiple files, formats, and systems (image scans, PDFs, paper charts, external referral packets).
- Delayed access to information: When records are buried in scanned documents or paper archives, clinicians or administrators may face delays retrieving critical information, which may impact care delivery.
- Limited analytics and insight: Unstructured or semi-structured document data cannot easily feed downstream analytics, predictive risk models, or population health programmes. This results in sub-optimal decision-making.
- Compliance and audit risk: Healthcare organizations must comply with regulations around patient privacy (HIPAA, GDPR), audit trails, redaction of sensitive data, and accurate documentation. Manual processes can increase risk.
- Burnout and cost: Clinicians often spend disproportionate time on documentation rather than direct patient interaction, which in turn increase frustration, burnout, and administrative cost.
Taking all these into account, it is obvious why automated, intelligent, structured document processing triumphs over the burden of manual, paper-centric workflows.
How AI helps in Automating Medical Documentation
The core idea behind the adoption of AI technologies is to digitize, extract, interpret, structure and integrate document-based data so that it can behave like traditional data in analytics, decision-support, audit, or operational workflows.
Key Technology Components
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
OCR forms the foundation for medical records automation. It is a technology used to analyze document images, identify text, and convert it into machine-readable format. In healthcare, OCR converts paper records into digital texts to be fed into electronic health records (EHR) systems. In addition to processing referral records, prescription forms and lab reports, it also uses specialized dictionaries to recognize complex medical terminologies. Advancements in the technology have made the modern OCR capable of handling different handwriting styles, detect different document layouts, and even read text from poor-image quality scans.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP enhances the capabilities of OCR by understanding the meaning behind the extracted clinical texts. This technology is used to analyze medical records for context to extract valuable information. They can identify diagnoses, symptoms, and treatments, recognize contextual nuances like negations (“patient denies chest pain”), and categorize information into structured fields for database storage.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning in healthcare essentially constitutes pattern recognition algorithms used for medical records extraction. These systems learn from previous examples to identify and classify medical information. They train on annotated datasets to understand how information should be extracted from different document formats. ML is also used for complex document reviews. AI data extraction and insights from historical datasets enable systems to learn to extract relevant information efficiently and provide deeper understanding from accumulated patient data. ML is a continuous learning software which can evolve on its own to recognize handwritings, different document templates and formats as it keeps processing more records.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA enhances the capabilities of other technologies by automating repetitive rule-based tasks. It essentially mimics human interactions with computer systems.
Core Capabilities of AI-driven Medical Documentation Automation
| Capability | What it does |
|---|---|
| Document Classification | Identifies type — lab report, prescription, consent form, etc. |
| Entity Extraction | Extracts key data: patient name, ID, diagnosis, date, medications. |
| Data Validation | Cross-checks with ICD-10 or CPT codes for accuracy. |
| De-identification | Removes PHI for research or data sharing. |
| Structuring & Export | Converts to interoperable formats for EHR or analytics tools. |
Benefits of Using AI for Healthcare Record Management
There are many benefits for automating medical records with AI, with some of the major ones being:
- Faster Access to Patient Data: Previously clinicians had to dig through physical archives or scanned PDFs. With AI, now they can easily search, retrieve, and analyze patient information instantly.
- Intelligent Test Result Handling: Laboratory and imaging results can be processed automatically, with critical values flagged for immediate attention and findings incorporated into patient records without manual data entry.
- Improved Accuracy: Machine learning in health care automation tools reduces manual entry errors, improving the integrity of clinical and billing data.
- Data Interoperability: AI converts diverse documents into standard data models (FHIR/HL7), ensuring seamless integration with EMR, billing, and analytics platforms.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Routine tasks like document organization, summarization, and claim validation can now be handled automatically, freeing human staff for higher-value work, and thereby reducing burnout of healthcare providers.
- Enhanced Patient Care: As AI reduces documentation time, clinicians can focus on direct patient interactions, complex decision-making, and comprehensive care planning, leading to better patient experiences and potentially improved health outcomes.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: By analyzing vast amounts of genetic data, AI can create targeted treatment plans. Unlike one-size-fits-all approaches, AI can detect genetic variations and recommend therapies tailored to an individual’s unique biology.
- Improved Collaboration and Quality: AI facilitates seamless data exchange between health care systems, enabling creation of comprehensive patient profiles, supporting collaborative care across providers, and assisting with quality initiatives.
- Enhanced Compliance: AI systems maintain audit trails, encryption, and automated redaction, ensuring compliance (HIPAA and GDPR).
-
- Cost Reduction: AI-driven automation cuts labor costs and minimizes claim rejections caused by data inconsistencies.
Use Cases across the Healthcare Ecosystem
| Sector | Use Case | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Hospitals & Clinics | Patient onboarding, clinical documentation, discharge summaries. | Faster processing and improved record accuracy. |
| Insurance Providers | Claims validation, preauthorization, fraud detection. | Reduced turnaround time and fewer claim disputes. |
| Public Health Agencies | National EHR digitization. | Centralized health data for analytics and planning. |
| Legal & Medico-Legal | Medical record summarization for case review. | Quick evidence extraction for litigation. |
| Pharma & CROs | Clinical trial data extraction. | Accelerated trial documentation and compliance (HIPAA and GDPR). |
Industry Examples and Impact
- US Healthcare Provider: A prominent healthcare provider in the US implemented RPA to cut down record processing time from 10-15 minutes to a few seconds. This improved productivity and they saved about $600,00o annually.
- Flatiron Health: Their models achieved 96% sensitivity extracting histology data from lung cancer patient records. This matches human-level accuracy while dramatically reducing extraction time.
- MarutiTech: They used NLP to process clinical notes, automatically extracting key medical entities like conditions, medications, and procedures. This greatly improved efficiency and accuracy.
- NHS (UK): AI-driven digitization reduced record retrieval time from 15 minutes to under 30 seconds per patient file.
- Cigna Insurance: Deployed AI-based claim document classification, improving approval accuracy and reducing fraud.
- Mayo Clinic (US): Leveraged NLP to automate extraction of clinical outcomes from 9 million notes, cutting manual review costs by 40%.
- Australian e-Health Research Centre: They combined the capability of OCR with NLP to convert unstructured pathology reports into structured data for cancer tracking.
- Apollo Hospitals (India): Implemented intelligent OCR for discharge summaries, reducing processing time by 70%.
Implementation Roadmap
Successful implementation of medical records automation requires a systematic and structured approach. The following is a step-by-step guide to do the same:
- Access Your Current Workflow: Evaluate your existing process before getting started on AI-driven automation. You can begin by documenting how records currently move through your system and then identify repetitive manual tasks and bottlenecks. Also review baseline processing times and error rates, and HIPAA requirements.
- Set Clear Success Metrics: Establish specific time and error reduction targets, cost-saving objectives, and staff productivity improvement goals.
- Choose High-impact Areas for Initial Automation: Prioritize high-volume, repetitive documentation tasks, and choose processes with clear, consistent structures. Also, identify areas with workflow inefficiencies that directly impact patient care.
- Prepare Technical Foundation: Begin with digitizing paper records using OCR and standardize data formats across systems. You should also establish secure connections between AI-driven automation tools and your EHR and configure role-based access controls to maintain security.
- Implement Phased Rollout: Starting small is the key. Let automation begin with a small pilot in a receptive department, and test thoroughly before expanding. Gradually scale to other departments after evaluating feedback and refining the system for optimal results.
- Train Your Staff: Provide role-specific training for different user groups and create accessible documentation and quick reference guides. You must also offer ongoing support during the transition period and emphasize on benefits to win approval from users.
- Monitor and Optimize Continuously: Track performance against your established metrics and regularly test system accuracy and workflow efficiency. Collect user feedback to identify improvement opportunities and also update processes as healthcare regulations evolve.
The above-mentioned steps would help you establish a robust AI-driven automation system while minimizing disruption and maximizing adoption among your healthcare staff.
Future of AI in Medical Records Management
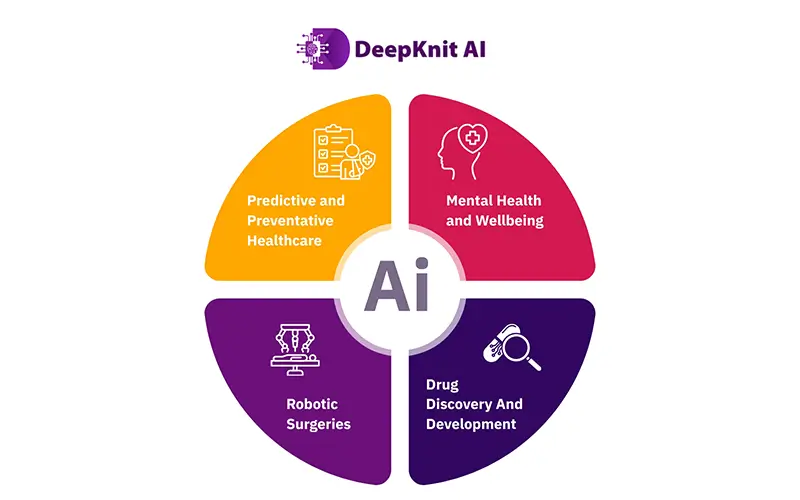
AI holds much for the future and we have only started scratching at the bottom of its possibilities. Here are a few futuristic predictions for the application healthcare AI:
- Predictive and Preventative Healthcare: AI makes proactive healthcare a reality by analysing patient data to predict disease risks before symptoms appear.
- Mental Health and Wellbeing: AI-enabled chatbots and therapy assistants are bridging the gap in mental health accessibility.
- Robotic Surgeries: AI-assisted robotics are enhancing surgical precision, reducing complications, and speeding up recovery time.
- Drug Discovery and Development: Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly turning to AI to accelerate the drug development process and streamline clinical trials.
With regards to medical records automation using AI, the next step would be augmentation and not just automation. Technologies like Generative AI and Decision Engines will let systems make patient journeys easier by detecting anomalies and recommending next steps for real-time diagnosis or billing validation.
Challenges in Automating Healthcare Documentation and How to Overcome Them
Besides the multitude of benefits that AI automaton can bring to medical record processing, there are certain concerns that need to be addressed.
- Data Privacy: The internet is a notorious place for data compromise and theft and hence data privacy and security remain a major concern when it comes to medical records automation. This can be mitigated by using on-premises or HIPAA-compliant cloud with PHI masking.
- Model Bias or Inconsistency: AI is only as good as the input data and hence prone to model bias inconsistency if the input data is not checked and revised for it. You can overcome this by continuous model retraining with diverse data.
- Integration Complexity: Having a great AI tool for your automation is one thing, but you must also make sure that it can seamlessly integrate with your legacy systems and operations. You can surpass this by adopting open APIs and FHIR-compliant interfaces.
- Resistance to Adoption: Even if you have all the above, it’s basically your workforce that’s going to use tis on a day-to-day basis, and you won’t be surprised to see that there are people who wouldn’t be willing to easily adopt the new technology. You can build their trust by beginning your AI automation journey with hybrid workflows (AI + human validation) and gradually progressing to full automation. Providing continuous training to your staff and making them aware about the benefits of AI automation can help you win their confidence.
Conclusion
While the implementation of AI can greatly enhance your organization’s efficiency, choosing the right technology and vendor plays a crucial role in implementing medical documentation automation. Your selection should match your organization’s specific needs, size, and capabilities. Make sure your preferred IT partner aligns with your security policies and IT infrastructure.
You can benefit from choosing AI solutions from established vendors like DeepKnit AI that can ensure faster implementation, ongoing vendor support, regular security updates, and compliance with healthcare regulations.
Bring the Power of Automation to Your Medical Records Processing.
Connect with a DeepKnit AI expert today.
Click here for a Consultation.