Data rules the roost in modern times. Unlike a decade ago, most of the modern-day businesses are data-driven. Data rules the roost in modern times. Unlike a decade ago, most of the modern-day businesses are data-driven.
From a simple text message (SMS) automatically generated by your bank intimating you about the spend you made after a unified payment interface (UPI) transaction, to clickbait notifications you receive in your handsets every other minute, the world generates about 402.74 million terabytes of data every single day. And, machine-generated data (automated data) accounted for over 40% of internet data in 2020.
Whether it is for business to customer (B2C), or business to business (B2B), imagine using spreadsheets to capture and process this humongous amount of data?
Business process automation (BPA) is the solution.
So, what is business process automation? Let’s learn what it actually is and what it is not.
Business Process Automation (BPA), Explained
To understand what business process automation (BPA) is, one must first have an idea about the various processes involved in their respective business like production (manufacturing), inventory management, financial processing (invoices, salaries etc.), employee onboarding and offboarding, marketing and sales lead generation, acquisition of new employees, and customer care among others.
The strategy of automating and syncing all needed but complex and repetitive business processes using software is called Business Process Automation (BPA). To streamline day-to-day operations to keep the business functioning smoothly is the main purpose of BPA. These “run the business” processes are the ones that generate revenue and help guarantee the efficiency of any business operation. These processes often cover multiple departments, the functions of which sometimes even converge and comprise a sequence of tasks that need partial or full automation.
BPA is different from other automation types as it is more complex and integrates multiple enterprise IT systems. It can use various technologies like robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), business process management (BPM), workflow orchestration, and cloud-based automation, and can be customized to the requirements of a particular business.
The objectives for implementing BPA in any business are enhancing operational efficiency, reducing human error, and standardizing processes, thereby allowing employees to focus on strategic tasks. By automating repetitive and manual processes, organizations can achieve greater productivity, efficiency, and cost reductions, which in turn enhance the overall business performance.
Types of Business Process Automation Technologies
Not all your processes require automation. Processes that involve repetitive, time-consuming, high-volume tasks are the best candidates for automation. Nevertheless, any stripe of business can benefit from the implementation of BPA.
Automation isn’t a one-size-fits-all process, and different processes or tasks may require different solutions. The type of automation solution you need depends on what task you require to fulfil, whether it’s a simple single task like data entry or an entire workflow across your organization.
Let’s take a look at 7 of the major types of BPA employed by enterprises today:
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA is the practice of using bots to perform repetitive, rule-based and high-volume tasks quickly. Examples of RPA include capturing digital signatures from online documents, processing large volumes of invoices automatically, or copying data between systems. RPA doesn’t involve tasks that require cognitive capabilities like data analysis, recognizing speech etc.
According to a report by Cflow Apps (November 2024), RPA adoption across industries has reached 31%, making it the most popular BPA technology in use today.
- Intelligent Automation
Using the latest technology like artificial intelligence (AI), natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML) or a combination of them is the most advanced form of automation. The advantage it has over other automation processes is that it has the capacity to learn on its own over a period of time, and can perform cognitive tasks like data analysis, visual identification, speech recognition etc.
A system that can identify product trends in the market and produce reports, or a chatbot that answers customer questions and routes complex issues to a human agent, are examples of intelligent automation.
- Enterprise Process Automation (EPA)
This is more complex and would require synchronization across multiple departments and systems to create a company-wide automation strategy. It helps keep all data consistent across different departments.
An example of EPA would be syncing customer data of a financial institution across their different departments like marketing, sales and other support teams so that everyone has the same information.
- Task Automation
Small but high-volume and repetitive tasks traditionally done by individuals can now be automated with the help of machines to reduce error and save time for them to focus on more strategic operations.
Generating automatic monthly reports on predefined dates or sending emails or SMS alerts to customers of a bank are examples of task automation.
- Workflow Automation
A group of tasks requiring a step-by-step process is automated using workflow automation to ensure that the correct order of work is being carried out by the related systems. It may require sync between different departments. While some tasks may be fully automated, others might need manual intervention and verification.
For example, when a customer places an order online, tasks like sending a confirmation mail with order details, checking the inventory for availability of the material, updating the inventory with stock details etc. would be done automatically. The system can also automatically sync with a secure online payment and generate shipping labels and packing slips. Nevertheless, the final steps involving packaging the right material, logistics and order delivery would require manual involvement.
- Process Automation
Process automation takes care of automating an entire process end-to-end with minimal human intervention rather than focusing on individual workflows. This type identifies as many modules of a process as possible, including both discrete tasks and overarching workflows that connect tasks and automate them for a seamless workflow. Process automation aims to optimize an entire process to ensure speed and consistency.
This type of automation usually supports financial transactions like online money transfer, or applying for a loan. A usual loan approval process involves application review, checking credit worthiness of the individual, document verifications, approvals, notification of whether loan is approved or rejected, and if approved, the final disbursal of the amount to the debtor’s bank account. This entire process can be done with minimal human intervention and process automation takes care of such tasks.
- Marketing Process Automation
Marketing is an important part of any enterprise as this is what finally brings in return on investment (ROI) that keeps the business running and paying your bills. Marketing involves various steps like market analysis, identifying the target audience, creating targeted messaging and reaching out to potential customers, lead generation, and more. Automating this entire process using intelligent tools like AI, ML, NLP etc. can benefit companies of any size.
For example, a smaller company may use this automation process to send out monthly emails to their target audience conveying relevant content, including discounts or offers. This would significantly reduce the number of hours spent on customer “touches” over the course of time. They can later scale this automation process to meet the requirements of their growing business. In the meantime, a larger firm can make use of extended marketing automation features like market analysis, dynamic segmentation of their extensive customer database, targeting of customers through a mix of direct mail, SMS or social media campaigns, measure impact of their marketing strategy and much more.
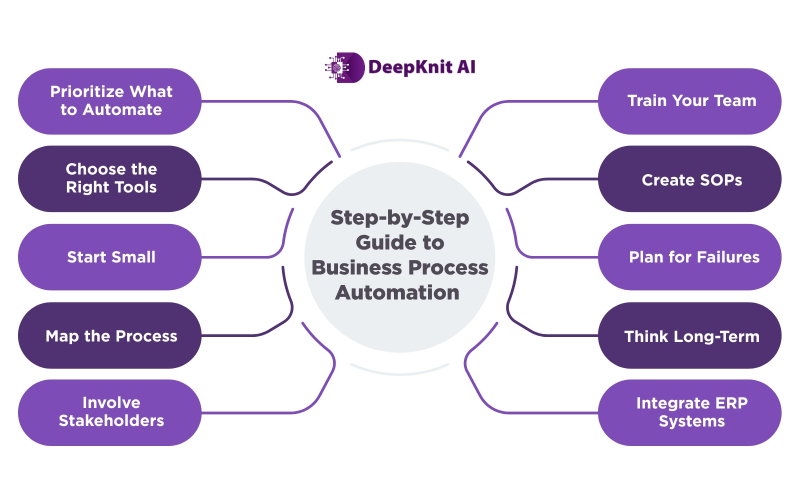
How to Implement Business Process Automation Step by Step
Here is an overview of the top 10 best practices to follow at every stage:
- Prioritize areas to automate: This is the first step you need to take before implementing BPA for your business. Not every function in your business process needs optimization. Prioritize areas to automate repetitive tasks that are high-volume and time consuming.
- Choose the right software: You might not need a full-stack BPA software to begin with. You might need just RPAs in some areas and AI in some others. Choose the right tools as per your requirements.
- Start small: This is an intelligent way to deploy automation in your organization. Look at the area/areas of priority that needs optimization and begin with that. You can scale up according to your needs at a later stage.
- Process mapping: Keep a record of the stages of your BPA implementation, measure results, and identify problem areas. This will save you a lot of time and money if you need to make changes at later stages.
- Involve stakeholders: It is always a good practice to involve the respective stakeholders early in the implementation process because they know the pain points much better than you. This would help in a more successful deployment.
- Train employees: Do not expect your employees to start using a new system effectively from the very beginning. You must identify the right talents, train and upskill them, all in parallel with your implementation process so that they would be ready to operate by the time it is up and running.
- Create SOPs: Realize that standard operation procedures (SOPs) are vital for achieving consistent results. SOPs not only help automation by providing clear descriptions of steps involved in a process, but also make it easier for people to move into new roles and fill in for each other.
- Have backup plans: Since you’re dealing with a new process, there are chances of trial and error. Have a contingency plan in place if the automation doesn’t go as expected.
- Have a long-term mind-set: Just because BPA worked well for business X doesn’t mean it will start giving immediate results to business Y. Have patience, follow due diligence, document everything, measure results, and be ready to make changes if something doesn’t give the desired results.
- Don’t forget ERPs: For many enterprises, enterprise resource planning (ERP) software plays an important role. It centralizes data from different teams, ERP integration with automation can give your BPA tools the information they need to run smoothly.
What Is Not BPA
Now, after having looked at what BPA is and how to implement it, let’s take a look at what is not BPA. Tasks where human judgment or creative problem-solving is vital, or complex decision-making is involved are generally not suitable for automation.
Also, it is:
- Not a job-killer: BPA is there to augment human capabilities and not to take away their jobs. It is only used to automate repetitive tasks which are high-volume so that people can invest their time and effort in bettering their strategic initiatives.
- Not a general solution: BPA works best when applied to specific, well-defined processes with clear inputs, outputs, and rules. It is not a one-size-fits-all solution for all your business challenges.
- Not about automating everything: Not all processes are ideal for automation. Tasks that require human discretion, judgement, empathy and creativity are better left for humans to handle.
- Not ideal for low ROI tasks: BPA tools are designed for high-volume, repetitive tasks, and are not fit for low volume but repetitive or disorganized (non-repetitive) tasks. It would be a waste of your investment to implement BPA for such tasks.
- Not a replacement for BPM: Business Process Management (BPM) involves a broader collection of methods for improving and optimizing business processes, including creative thinking, complex problem solving, analysis, and redesign. BPA is only a subset of BPM that focuses specifically on automation to enhance the latter.
- Not a replacement to ERPs: Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software are big-picture business management solutions. However, you can integrate BPA tools with your existing ERP to enhance functionality.
Benefits of Automating Business Processes
Businesses of all kinds and sizes can benefit from automation. However, enterprises must consider factors like scope for scaling, training the staff for a seamless integration of the automation into their workflow, and most importantly identifying the areas they need to automate as all processes (especially of smaller or midsize establishments) may not require, or not worth investing in automation.
Nevertheless, automation brings to businesses the following benefits:
- Cost saving: Since machines are, well machines, they excel at performing repetitive tasks without fatigue, leading to lower error rates and more consistent output quality. This would lead to better ROI over a period of time.
- Enhanced efficiency and accountability: The adoption of a cloud-based automation tool can help with centralized data storage, which can be accessed anytime from anywhere. This level of access grants businesses the advantage of real-time tracking, thereby improving accountability.
- Compliance and transparency: Automated processes have the advantage of tracking and recording every procedure, which helps in sticking to regulations and compliance rules easily. These records come handy during audits, which in turn gives more transparency to your organizational functions.
- Customer satisfaction: Automation brings smoother and seamless processes which ultimately results in better customer experience with faster responses and fewer errors. Your customers would reward you for this with their loyalty, positive recommendations and ultimately more business.
Top 5 Challenges of Implementing BPA
However beneficial it can be to your business, just like any other new technology, BPA comes with some challenges too. Below are the top 5 challenges you’re likely to face while implementing BPA to enhance your business.
- Initial cost: Many might have led you to believe that the initial cost of implementing BPA to your legacy systems can be troublesome and quite expensive. Well, they are neither entirely wrong nor right. It is true that the initial cost of setting up a BPA system for any business is quite high. However, intelligent implementation of BPA after considering your requirements and budget can improve your profits over a period of time as you would be saving a lot of time, resources and money spent on traditional systems.
- Complex implementation: Any BPA is only as good as the set of data you input while implementing it. This is time consuming and the chances of automation not giving the desired results is high if not set up properly. Bringing all respective stakeholders on board early on into the implementation process can save you this trouble.
- Resistance to change: It’s not just your legacy systems that might have problems adapting to change but also your employees. Some of them may fear that machines are going to eat up their jobs and hence resist the change. Making them understand the benefits of automating business processes, and giving proper training to upskill them to work with machines is a business practice that all enterprises with a vision for the future must do.
- Lack of flexibility: Unless coupled with an AI agent, automated systems don’t have adaptive memory and are governed by set rules and instructions. Automation can slow things down in an episode of unexpected events or if you need to make quick changes. You can avoid this by choosing a system that gives you regular updates and can handle exceptions.
- Overdependence on tech: As automation is implemented across various systems to seamlessly work together, any disruptions like a power failure, cyberattack or system crashes can bring about a cascading effect. Make sure to have fail-safe measurements in place like power backup, strong cyber security systems and others.
Conclusion
For many people BPA is a go-to solution for all their business challenges but this is a general misconception. BPA is great if you implement it intelligently, and it would enhance your BPM or ERP solutions.
As the BPA ecosystem keeps evolving, DeepKnit AI enjoys a special position in implementing innovation at any level for companies of any size. With years of experience in successfully deploying BPA solutions for many businesses, DeepKnit AI can tell you how to choose the right BPA software for your business and get the maximum out of it.
Bring intelligent automation to your operations.
Consult us for the right set of BPA tools for your business.