The influence that artificial intelligence (AI) now has on our day-to-day lives is immense. It has taken over and changed the way we work, think, communicate, travel and even how we entertain ourselves. Needless to say, besides industries like manufacturing, logistics, retail, finance and others, it is also redefining the healthcare sector in more ways than one.
In the healthcare sector, personalized or precision medicine—where treatments are tailored to each patient based on their unique traits—has long been a concept that remained unrealized. However, AI-driven personalized medicine is now turning this idea into reality.
Keeping up with the fast pace of new drugs, treatment protocols, and changing regulations is difficult for healthcare professionals. AI helps overcome this challenge by analyzing large amounts of data quickly and providing useful insights in real time, which supports better and faster decision-making.
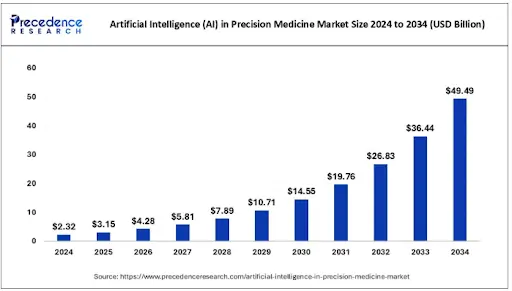
The influence of AI in personalized medicine is on the rise, and a report by Precedence Research says that “The global artificial intelligence (AI) in precision medicine market size was accounted for USD 2.32 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 49.49 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 35.80% from 2025 to 2034. The artificial intelligence (AI) in the precision medicine market is experiencing significant growth due to the increasing demand for personalized treatments.”
Let’s delve deeper into the subject and see how AI is driving personalized medicine, the role of genomics, key technologies involved, and its applications and benefits.
Understanding Personalized Medicine and the Role of AI
For many years, healthcare has largely followed general treatment methods that are intended to work for most people. However, it is well known that people react differently to medications based on factors like their general health, genetic makeup, tolerance or resistance levels, and other unique characteristics.
Personalized medicine, also known as precision medicine, involves tailoring medical treatments, interventions, and care plans based on an individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, environment, and biological markers.
Thanks to AI, doctors can now identify patients with special health profiles or unusual responses to treatments by combining genetic, clinical, and lifestyle data. AI plays a vital role in this process by using advanced algorithms and powerful computing systems to discover complex patterns and generate insights that improve medical decisions on a large scale.
Recent research highlights the value of combining genomic and non-genomic factors, such as symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle, in enabling more accurate diagnoses and predictions that are specific to each patient. This integrated approach helps address major challenges in precision medicine and speeds up its real-world application.
In practice, precision medicine fits into an organization’s workflow by assigning appropriate tasks to different members of the clinical team.
Routine tasks may be carried out by nurses, medical assistants, or administrative staff, while complex data-driven insights are shared with healthcare providers, ensuring that the most appropriate care decisions are made by the right people at the right time.
How AI Tailors Treatments Based on Genetic Profiles
Genetics plays an important role in deciding how the body responds or reacts to certain drugs, how diseases develop, and how patients respond to different treatments. For example:
- Certain drugs act too quickly or too slowly on some individuals, and this is because of mutations in liver enzyme genes.
- In cancer treatment, finding out the specific cancer mutation helps in deciding the most effective chemotherapy drugs.
- Also, genomic markers can point out an individual’s susceptibility to chronic illnesses such as diabetes, Alzheimer’s, or cardiovascular disorders.
Integrating genetic insights into medical decision-making has tremendous benefits, but it requires processing vast amounts of data, and this is where AI plays a crucial role.
Role of AI in Revolutionizing Disease Detection and Diagnosis
Fast and accurate diagnosis decides the effectiveness of any treatment. Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the detection and diagnosis of disease by lowering diagnostic errors and by augmenting medical practitioners’ skills. With the help of AI systems, clinicians can now examine patient data, spot minor patterns as well as early disease symptoms.
For example, AI can examine medical imaging such as MRIs and X-rays in detail to find anomalies that the human eye might miss. Moreover, AI-driven diagnostic technologies can optimize surgical results by offering real-time analysis and suggestions during procedures.
Healthcare professionals can identify high-risk individuals and put preventive measures in place to slow the spread of disease because of AI’s capacity to process and analyze vast datasets and create predictive models. This brings a more proactive than reactive approach to healthcare.
Applying the Power of AI in Medicine and Healthcare
The healthcare industry is witnessing a shift from generalized to personalized medicine driven by AI algorithms that can analyze enormous volumes of patient data, including genetic information, medical history, lifestyle factors, and real-time data.
This information can be used to:
- Optimize Treatment Plans: AI in precision medicine helps in treatment optimization plans for each individual patient after factoring in details such as genetics, health history, and lifestyle. This improves outcomes and minimizes side effects. For example, AI can personalize asthma management by adjusting medication types and dosages based on patient-specific triggers and responses.
- Predict Disease Risks: By analyzing genetic, clinical, and lifestyle data, AI can predict a person’s susceptibility to certain diseases, thereby enabling early intervention and preventive care. For example, AI can identify patients at substantial risk for type 2 diabetes, prompting lifestyle changes or monitoring before symptoms appear.
- Enable Precision Medicine: AI can analyze a patient’s unique genetic and clinical profile to enable precision medicine, enhancing drug efficacy and reducing side effects. For instance, AI can detect a tumor’s genetic mutations and analyze the patient history to recommend the most suitable cancer therapy.
- Enhance Patient Engagement: AI-powered virtual health assistants can deliver personalized education, reminders, and real-time support, thereby enhancing patient engagement. For example, a virtual assistant can guide a diabetic patient with daily glucose tracking, meal suggestions, and medication reminders, fostering better self-management and adherence.
- Accelerate Drug Discovery: AI in personalized medicine can identify potential targets and predict compound effectiveness, significantly reducing research time and cost. This helps in accelerating drug discovery. For example, AI algorithms have helped uncover new protein targets for Alzheimer’s, speeding up the development of promising therapeutic candidates.
- Assisting Patients in Navigating the Healthcare “Maze”: AI simplifies healthcare navigation by providing personalized insights into a patient’s health plan, such as flagging when prior authorization is needed or confirming in-network referrals.
How AI Powers Personalized Medicine
AI brings the power of fast computation, automation, and predictive analysis to healthcare. It supports real-time clinical decisions by interpreting genetic sequences and identifying patterns that human eyes could miss.
Some of the real-world manners in which AI supports personalized medicine are as follows:
Genomic Sequencing and Analysis
AI tools with deep learning capabilities and transformer-based systems can:
- Annotate genes and identify functional impacts.
- Predict gene expression and regulatory patterns.
- Detect mutations and rare genetic variants with high precision.
- Compare individual genomes against large population datasets.
AI makes precision medicine scalable by reducing the time and cost of genomic analysis.
Machine Learning for Predicting Risks
By analyzing genomic sequences, clinical, lifestyle, and environmental factors, AI models can predict the early onset of diseases before even the symptoms show up. Examples include:
- Predicting the possibility of diabetes and its complications.
- Identifying individuals at high risk of certain heart conditions like cardiomyopathy.
- Forecasting hereditary cancer risk based on BRCA1/BRCA2 and other gene variants.
AI for Drug Response Prediction (Pharmacogenomics)
Pharmacogenomics is that branch of pharmacology that explores how genes influence drug responses. AI enhances this field by:
- Predicting adverse drug reactions.
- Optimizing drug dosage for individuals.
- Identifying genetic markers that affect drug metabolism.
- Recommending alternative drugs based on genomic insights.
AI in Biomarker Discovery
Clinicians can improve their diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment optimization plan of a patient with the help of biological indicators called biomarkers. AI helps in identifying these biomarkers by analyzing multiple datasets such as:
- Genomics
- Proteomics
- Microbiomics
- Metabolomics
- Transcriptomics
This multi-layered approach leads to more precise, stratified treatment plans.
Key Technologies behind AI-driven Personalized Medicine
Genetically tailored treatments are made possible by a combination of several advanced technologies like:
Genomic Sequencing Technologies
Tools such as whole-genome sequencing (WGS), whole-exome sequencing (WES), and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) are used to capture large-scale genetic and molecular data. Advancements in next-generation sequencing (NGS) have made these technologies faster and more affordable.
AI and Machine Learning Models
AI models frequently used in personalized medicine include:
- Deep neural networks.
- Ensemble learning for risk prediction.
- Transformer architectures for DNA sequence modeling.
- Graph neural networks (GNNs) for molecular interactions.
- Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for genome interpretation.
These models process complex datasets and generate actionable insights for clinicians.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Integration
All information relating to a patient, such as medical histories, lab results, and imaging scans, is stored in EHR systems. Integrating this data with genomic information with the help of AI offers comprehensive risk and treatment predictions.
Knowledge Graphs and Biological Networks
Knowledge graphs map relationships between genes, proteins, drugs, and diseases. They support:
- Automated hypothesis generation.
- Understanding complex disease pathways.
- Identification of drug repurposing candidates.
Cloud Computing and High-Performance Computing (HPC)
Large-scale data storage and computing power are essential for genomic insights. Cloud-based infrastructures enable:
- Real-time genomic processing.
- AI model training on massive datasets.
- Secure data sharing and collaboration across institutions.
AI-driven pharmacogenomics ensures that patients receive safe and effective therapies tailored to their genetic makeup.
Applications of AI-based Personalized Medicine
AI-powered personalized medicine finds its application in nearly all branches of healthcare.
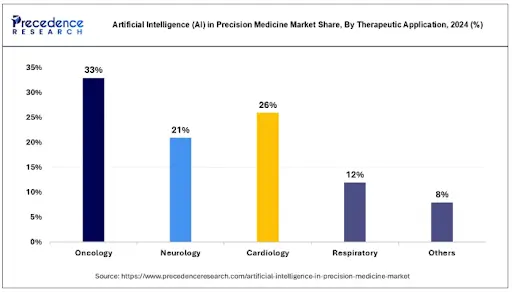
Oncology: Personalized Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatment has gained much from AI-driven precision medicine. Cancerous cells/tumors vary widely at the genetic level, and AI helps ensure individualized treatment optimization. AI in oncology helps in:
- Tumor gene sequencing: AI can identify mutations that cause the cancer.
- Targeted therapy recommendations: AI can match drugs suitable for corresponding genetic profiles.
- Immunotherapy response prediction: AI can predict the response of checkpoint inhibitors in patients.
- Minimal residual disease (MRD) detection: AI helps identify microscopic cancer remnants.
- Precision radiology: Tumor characteristics can be better studied using enhanced imaging analysis by AI.
Cardiovascular Care
Cardiovascular diseases have marked genetic roots. AI helps by:
- Predicting arrhythmia risk.
- Personalizing anticoagulant dosages.
- Identifying familial hypercholesterolemia.
- Forecasting heart failure progression using genetic and imaging data.
Neurology and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Conditions such as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and muscular dystrophy are influenced by genetics and complex biological interactions. AI enables:
- Personalized cognitive decline predictions.
- Genetic risk scoring for neurodegenerative diseases.
- Biomarker identification from brain imaging and genomic data.
Pharmacogenomics in Clinical Practice
AI helps in personalizing drug prescriptions for conditions like:
- Chronic pain
- Hypertension
- Depression and anxiety
- Autoimmune diseases
This reduces adverse reactions and improves treatment outcomes.
Precision Nutrition
AI matches genetic markers with dietary needs, enabling personalized diets for:
- Diabetes management
- Gut health optimization
- Weight management
- Food intolerance prevention
Infectious Diseases and Immune Response Modeling
AI can be used to analyze genetic variations that influence immune responses, which helps in personalizing vaccination and treatment strategies for individual patients.
Rare Diseases and Undiagnosed Conditions
AI models can identify rare mutations by analyzing whole-genome data and medical histories. This significantly helps in detecting conditions that were historically overlooked.
Healthcare Workflow Automation with AI-driven Insights
Personalized medicine in healthcare is made possible through a structured workflow that combines clinical, genomic, and computational processes.
Step 1: Data Collection
This is the first step, where data is collected from different sources such as:
- Genetic sequencing data
- Clinical data from EHRs
- Medical imaging
- Lifestyle and social determinants
- Wearable device data
Step 2: Data Integration
AI platforms collate data from different sources to form a comprehensive patient profile.
Step 3: AI Analysis and Interpretation
AI models perform the following tasks:
- Disease risk scoring
- Drug response prediction
- Variant calling and interpretation
- Treatment recommendation modeling
Step 4: Clinical Decision Support
This is an important stage where clinicians are presented with explanations, confidence levels, and alternative therapy suggestions by the AI.
Step 5: Personalized Treatment Delivery
Clinicians use AI insights to:
- Tailor drug choices
- Define dosage levels
- Identify monitoring plans
- Recommend lifestyle changes
Step 6: Continuous Monitoring and Model Updates
The buck doesn’t stop with prescribing the right personalized medicine but the AI systems will continuously refine predictions based on:
- New patient data
- Updated genomic science
- Treatment response outcomes
Benefits of AI-driven Personalized Medicine
AI-driven personalized medicine is making healthcare shift from one-size-fits-all treatments toward precision care tailored to each individual. By using genetic data, biomarkers, and advanced machine learning models, AI helps clinicians predict risks, choose the right therapies, and optimize outcomes with unprecedented accuracy.
The benefits of AI in precision medicine are as follows:
- Precision Treatment Tailored to the Individual: AI can analyze genomics, biomarkers, lifestyle data, and medical history to tailor treatment plans uniquely matched to each individual.
- Efficient Analysis of Medical Imaging: AI algorithms process X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs with not just unmatched speed but also precision, which helps radiologists in identifying conditions that might otherwise be missed.
- Early Detection and Predictive Diagnosis: Machine learning models can identify disease risks before symptoms appear, enabling prevention or early intervention.
- Optimized Drug Selection and Dosage: Pharmacogenomic helps in determining which drug will work best for a specific genetic profile. This enables safe and the most effective dosage, also reducing trial-and-error prescribing.
- Reduced Adverse Drug Reactions: Since AI can spot genetic incompatibilities and predict potential side effects, the risk of adverse drug reactions is reduced.
- Faster Clinical Decision-Making: AI processes massive datasets instantly, giving clinicians real-time insights that typically take hours or days.
- Enhanced Treatment Monitoring: Real-time treatment adjustments are now possible with wearables and health sensors sending continuous feedback to AI systems.
- Streamlining Multidisciplinary Collaboration: AI tools make sharing data across different teams easier, thereby improving communication and decision-making within care teams. Enhanced collaboration supports more holistic and coordinated treatment optimization plans.
- Cost Efficiency: By preventing complications, reducing hospitalizations, and minimizing ineffective treatments, personalized medicine lowers overall healthcare costs.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Personalized medicine leads to higher treatment success rates, better disease management, and improved quality of life.
- Accelerated Research and Clinical Trials: AI helps in identifying ideal trial participants and simulates biological responses, helping pharma companies to speed up the time required for clinical trials.
- Improved Patient Engagements: AI provides patients with highly customized health insights and recommendations, which in turn increases their engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
It is true that AI in personalized medicine has tremendous advantages, but it also comes with certain challenges, which are:
- Data Consistency: Since AI integrates with different sources, the data that comes into the system may not be of the same format. Extensive data cleansing and standardization are required for the smooth running of an AI system.
- Data Privacy: One of the major concerns in AI for personalized medicine is the privacy and security of the data used for the process. Patient data is sensitive information, and organizations make sure that their AI systems strictly comply with all HIPAA and GDPR regulations to ensure data privacy and security. Unauthorized access or breaches in medical databases could lead to misuse of sensitive health information, emphasizing the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
- Data Bias/Hallucination: This happens especially if the AI systems are not trained in unrepresentative or edge data also, in which case they would produce skewed results, leading to disparities in treatment recommendations. Addressing this issue requires the inclusion of diverse datasets that account for different demographics, ethnicities, and genetic variations.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Regulatory hurdles also present a significant barrier to AI adoption in personalized medicine. The absence of standardized regulations and approval frameworks for AI-driven medical applications slows down their integration into clinical practice. Establishing globally accepted regulatory guidelines is crucial to ensuring AI tools are reliable, safe, and ethically sound for widespread medical use.
- Staff Training: Yet another challenge in AI for personalized medicine is the reluctance of staff to adopt to a new technology or they mistrust the results given by it. You need to make sure that sufficient training is given to your staff to make them start believing in using a revolutionary system that would enhance their efficiency.
Conclusion
AI-enabled medical practices offer a path to greater efficiency, better clinical decision support, and a more satisfying patient experience. The integration of AI in healthcare not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also helps in deriving proactive, data-driven clinical decisions that improve patient outcomes and reduce overall healthcare costs.
To fully leverage this potential, healthcare organizations need tailored digital solutions. DeepKnit AI’s healthcare solutions are designed to address critical pain points such as fragmented data, delayed diagnoses, and patient engagement gaps. From building intelligent clinical support software to crafting HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare platforms, we help you deliver precise, scalable, and patient-centric care.
Precision Care Powered by AI.
Empower Your Healthcare Journey with AI-driven Innovation.
Reach an expert